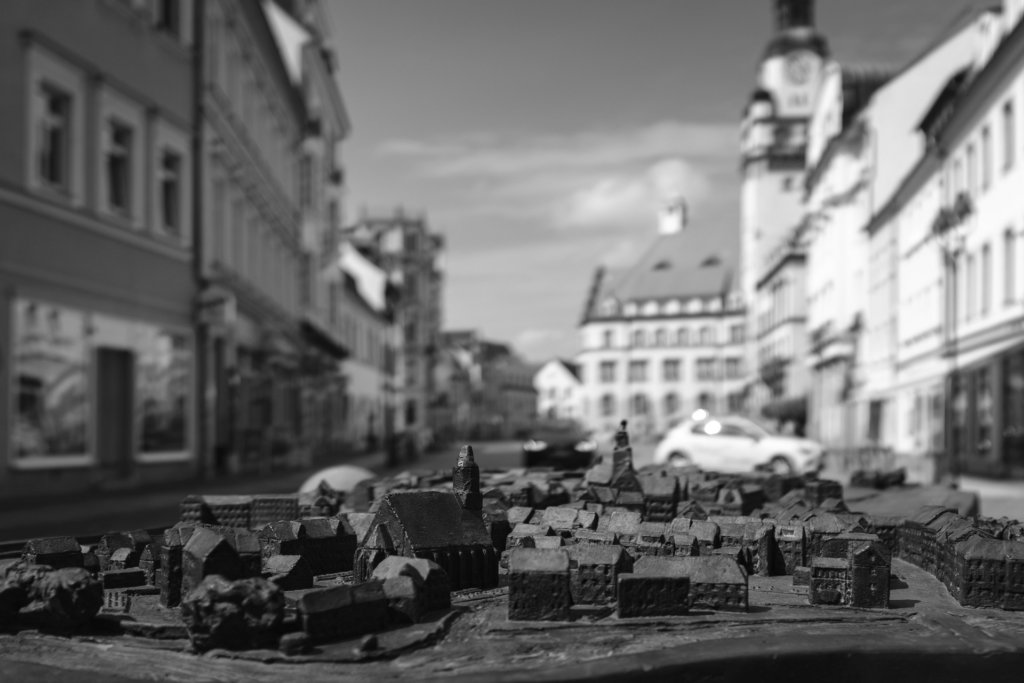
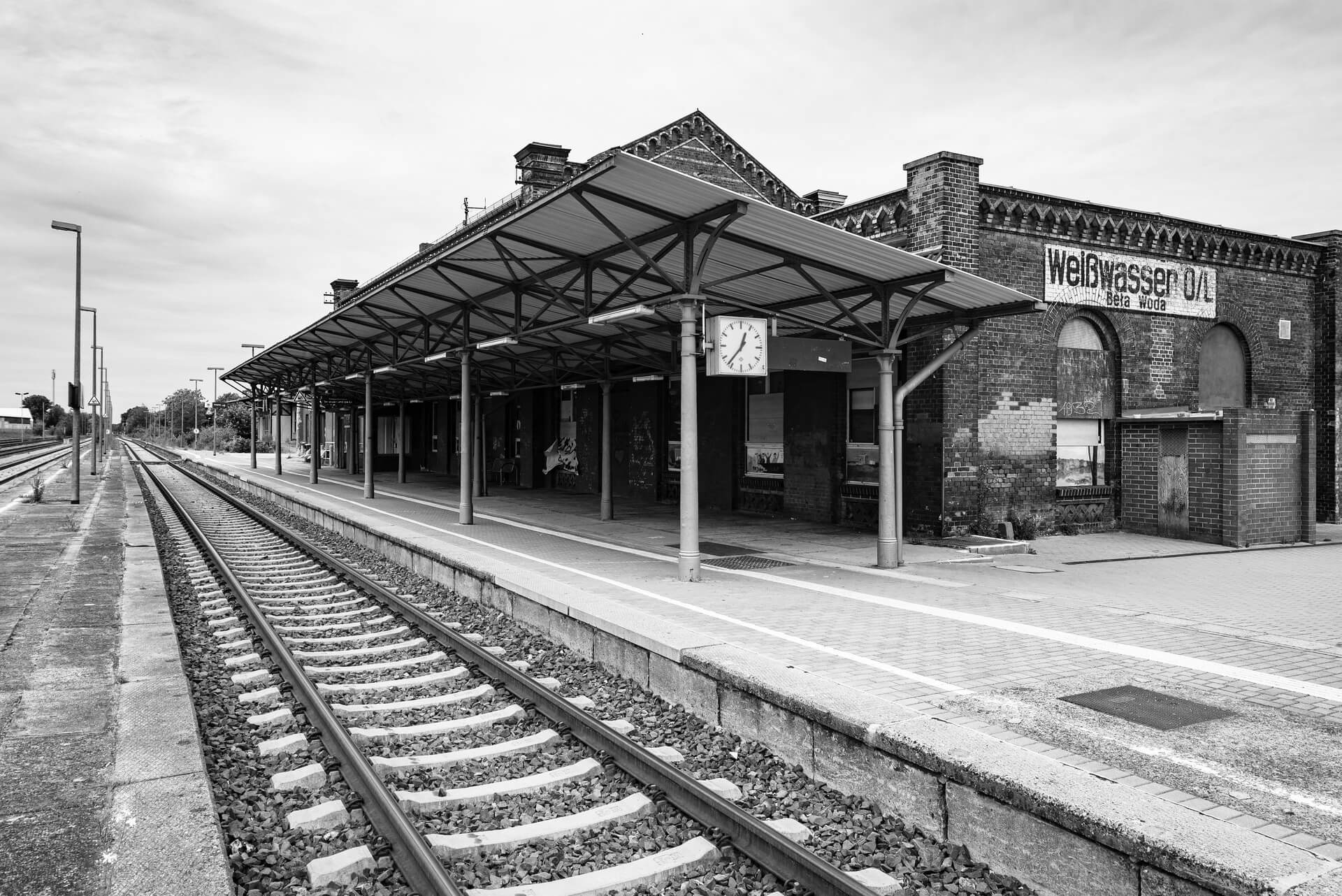
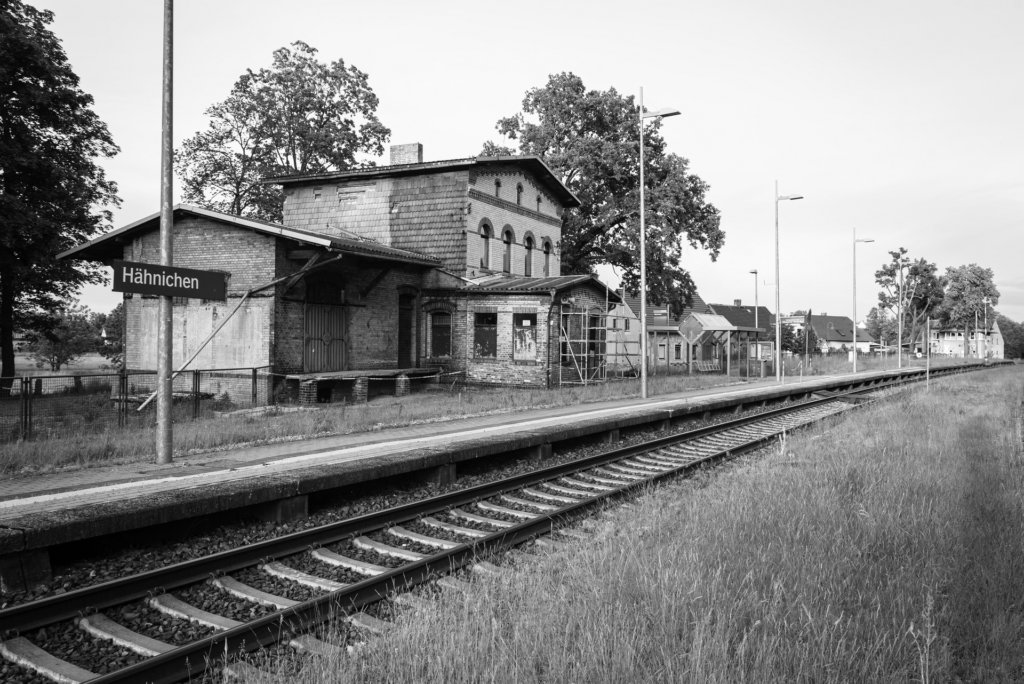
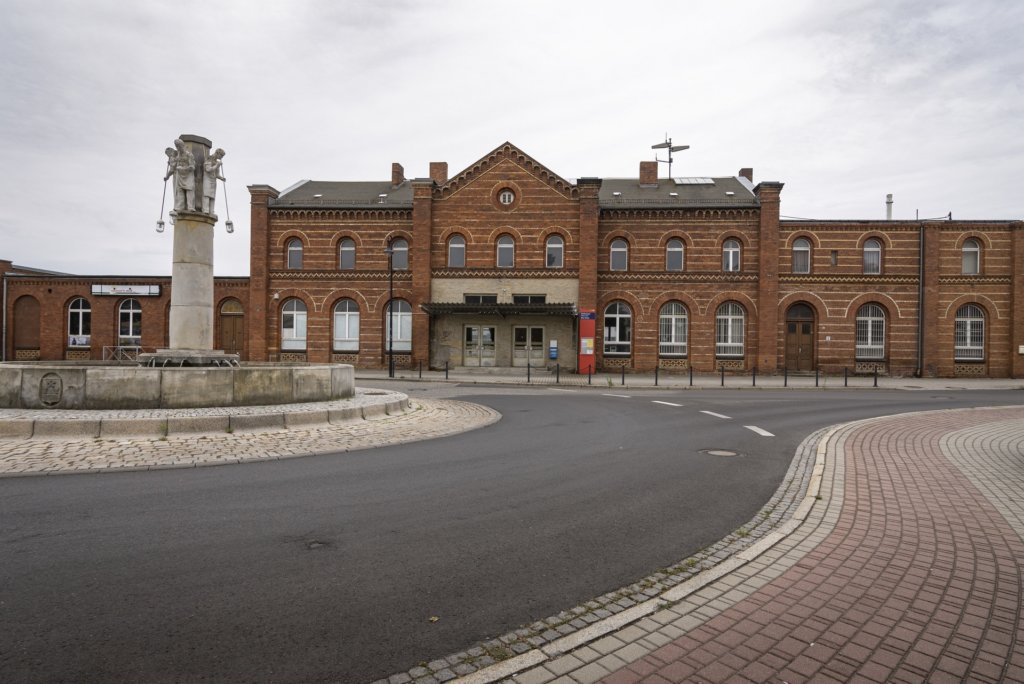
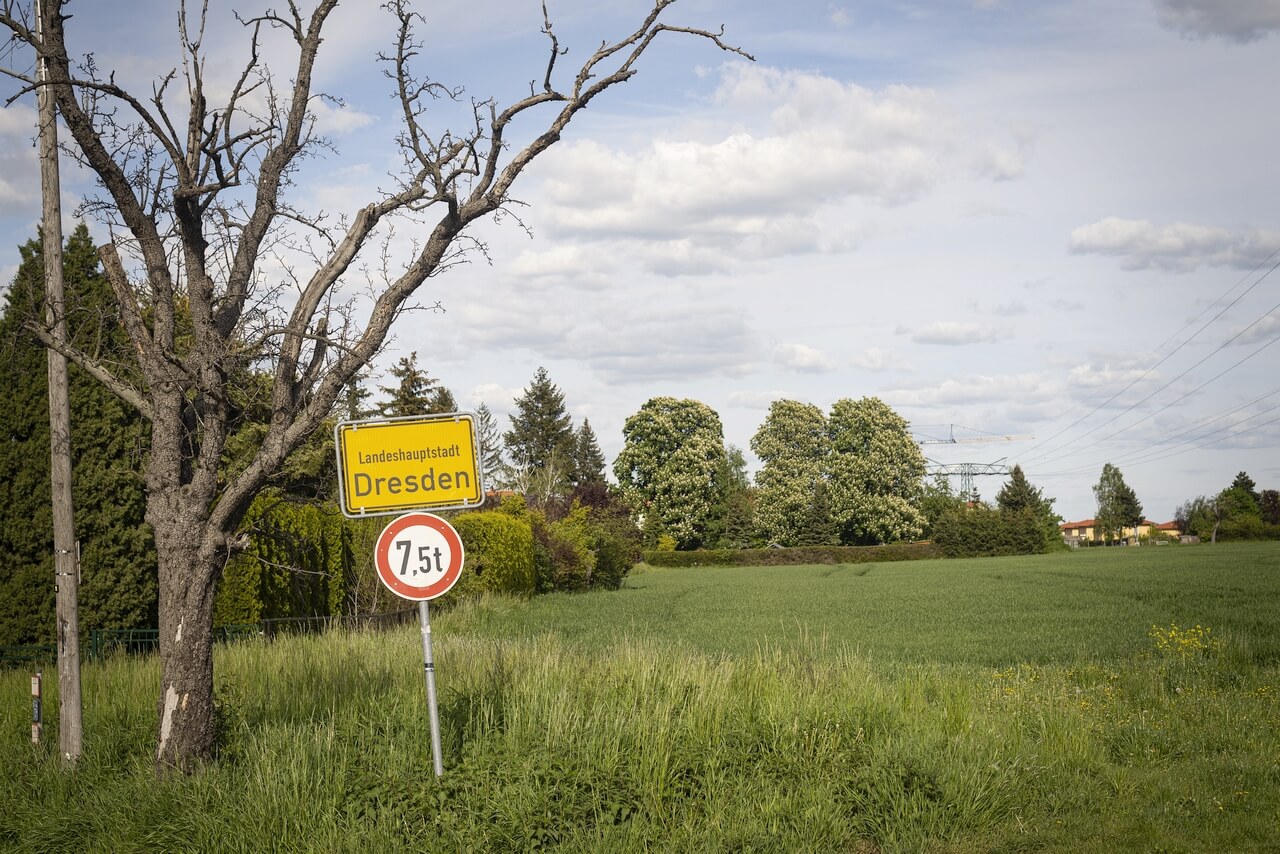
GUBEN – “PEARL OF LOWER LUSATIA”,
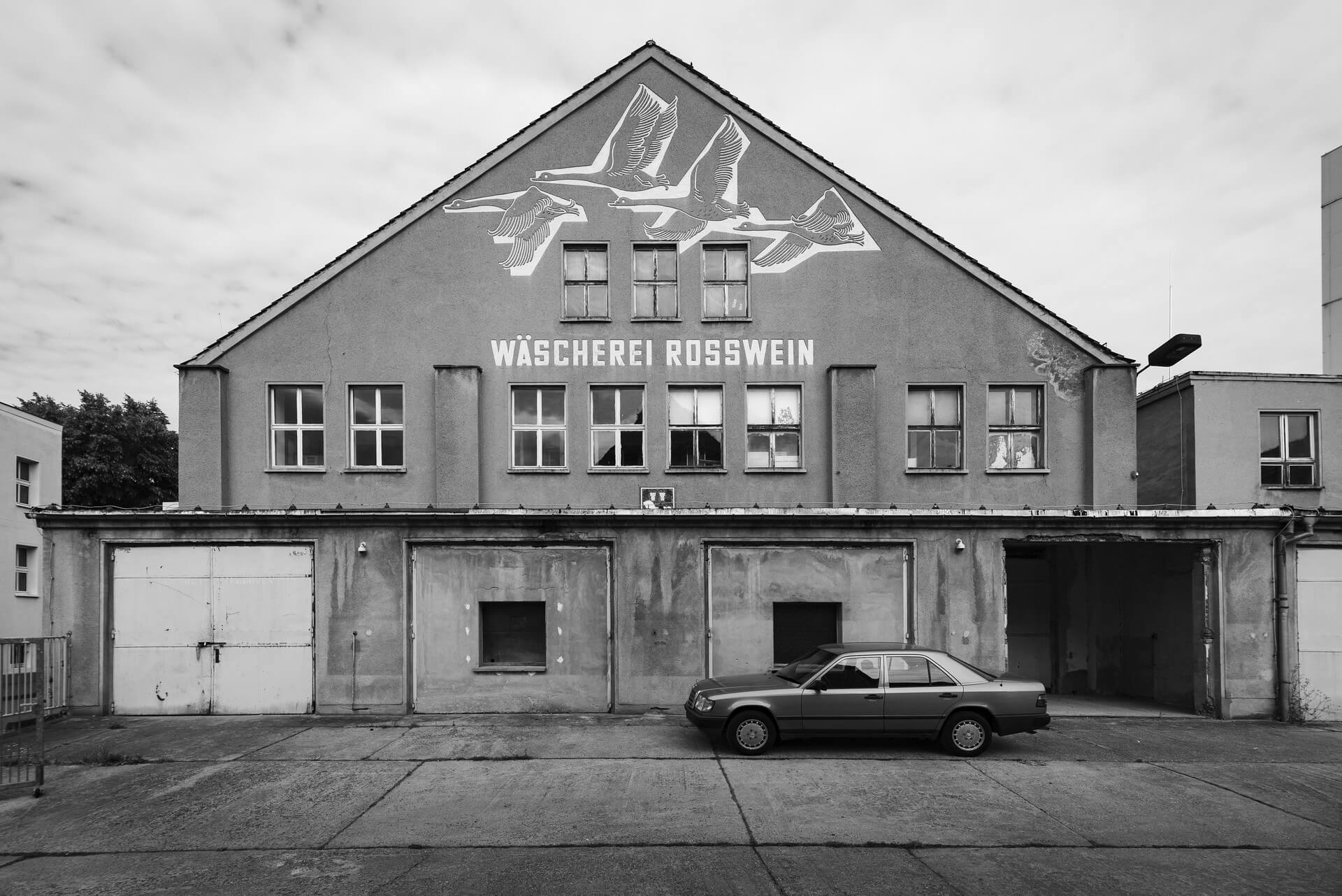
a historical title, today disputed and only used by a few local patriots and local historians in reference to their town, certainly had its justification in the past, at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th century. During this time, the town on the Neisse experienced its heyday, the textile industry, above all the millinery industry, brought considerable prosperity to the town, and in 1874 the Guben municipal theatre opened – today you have to drive at least 25 km to go to the next cinema.
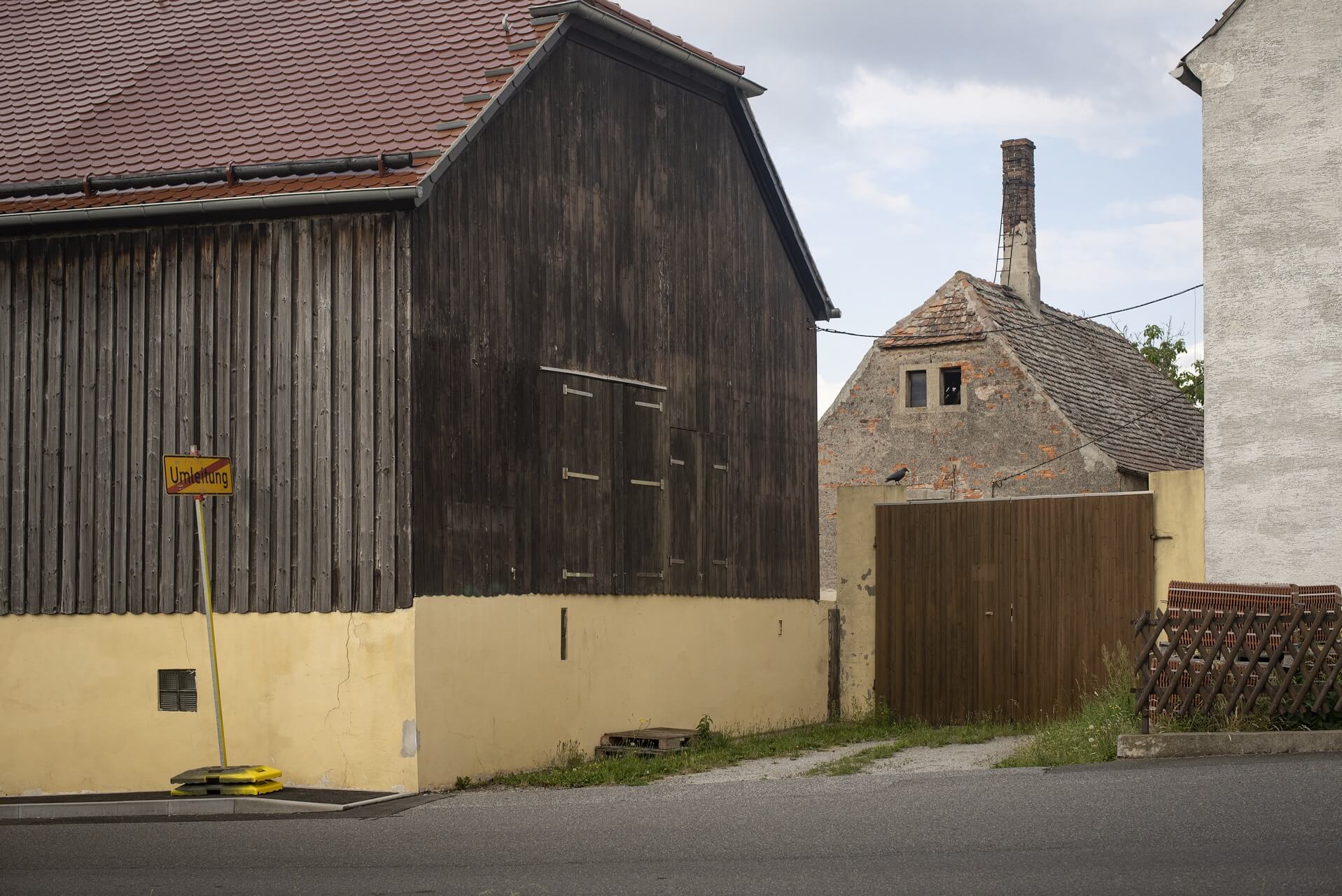
The first decline came at the end of the Second World War; in the spring of 1945, heavy fighting raged here for two months, as a result of which 90% of the buildings were damaged and in large parts completely destroyed. The end of the war also changed the course of the border, the Neisse and Oder rivers formed the new eastern border of post-war Germany, and Guben effectively became two towns: Gubin, with its former town centre, on the east bank of the Neisse, and Guben, the predominantly industrial suburb, on the west bank. The German inhabitants had to leave the eastern part, which was assigned to Polish people, who in turn were expelled from eastern Poland, which henceforth became part of the Soviet republics of Belarus and Ukraine.
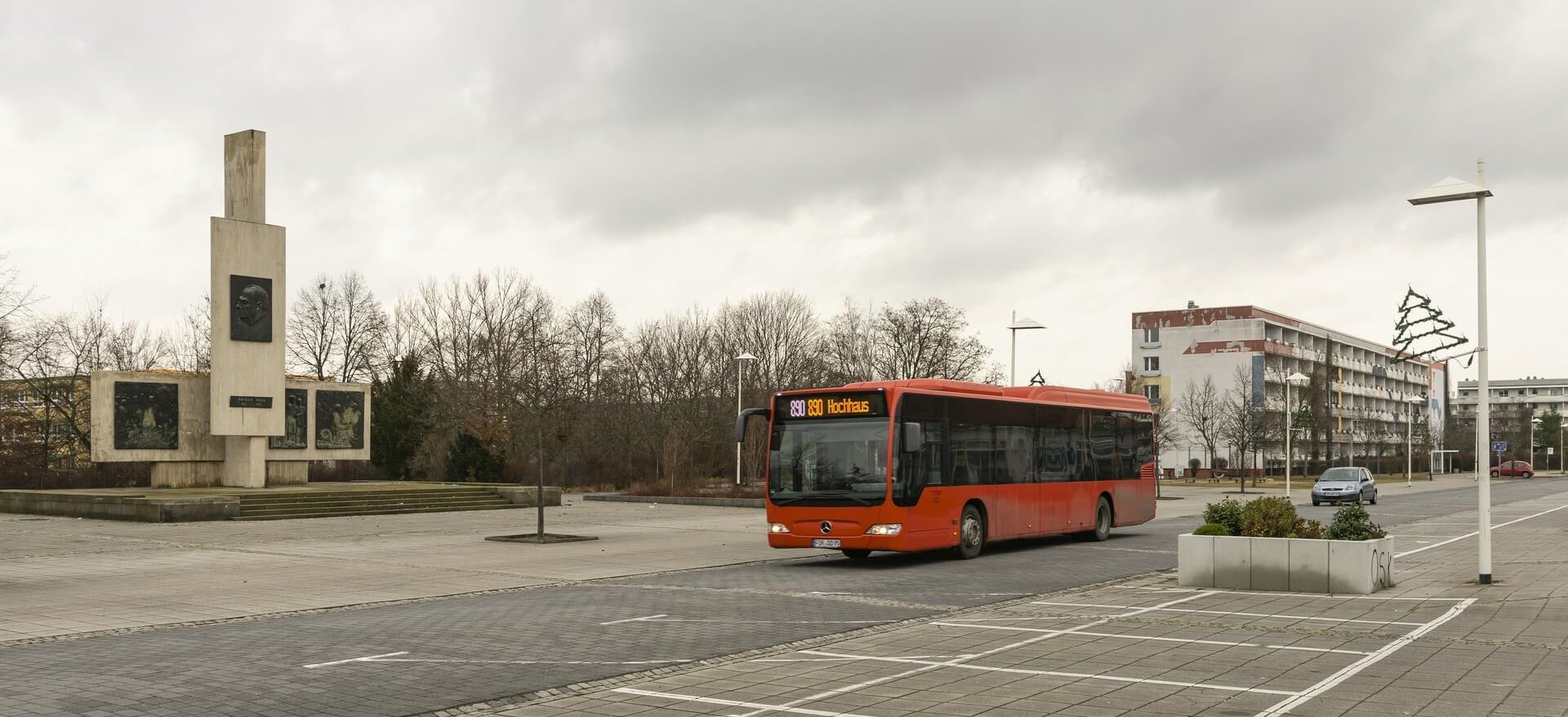
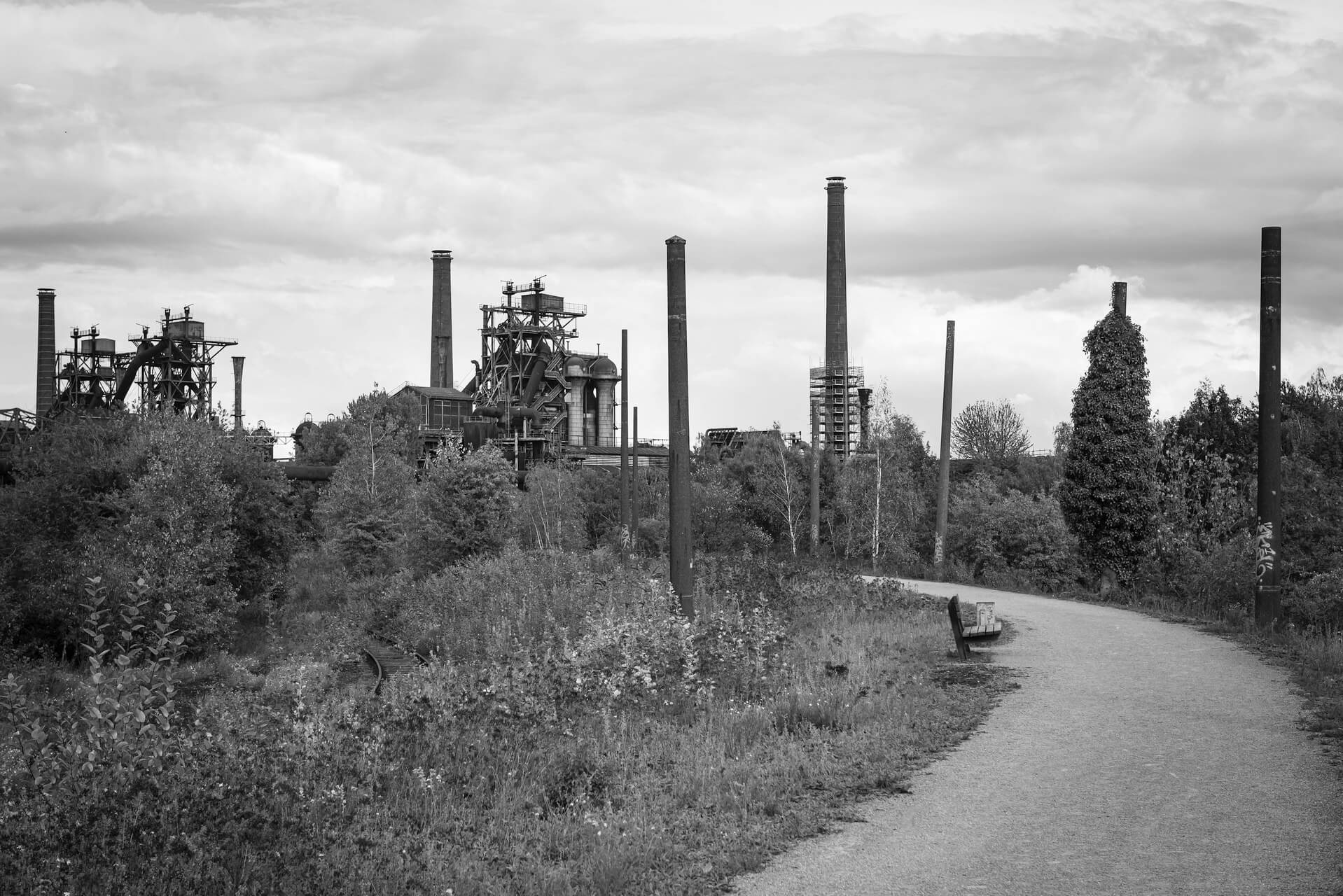
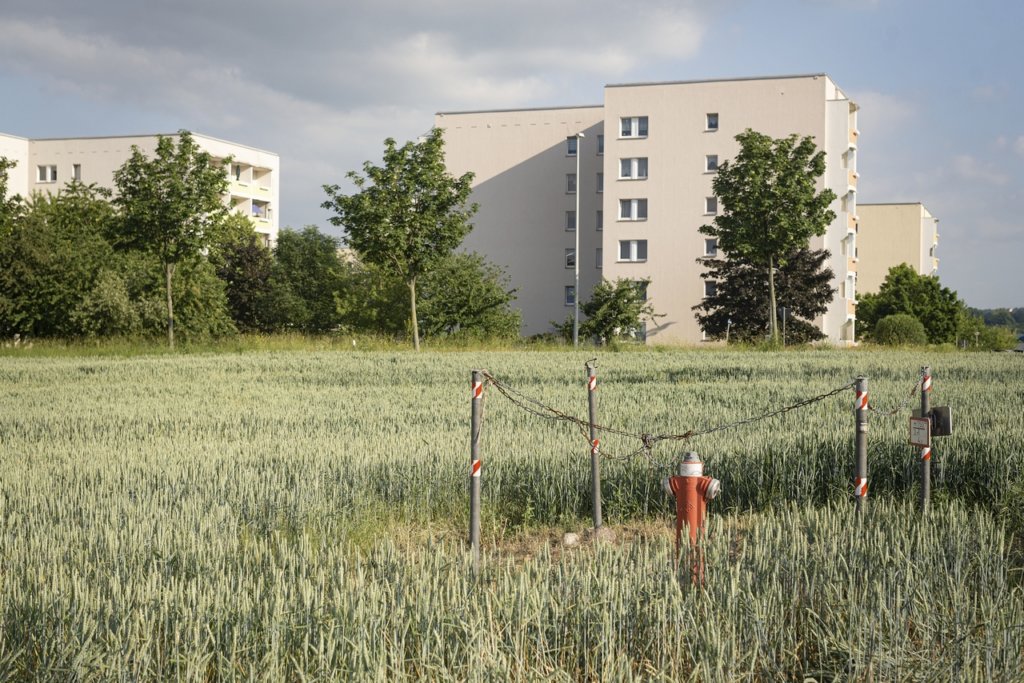
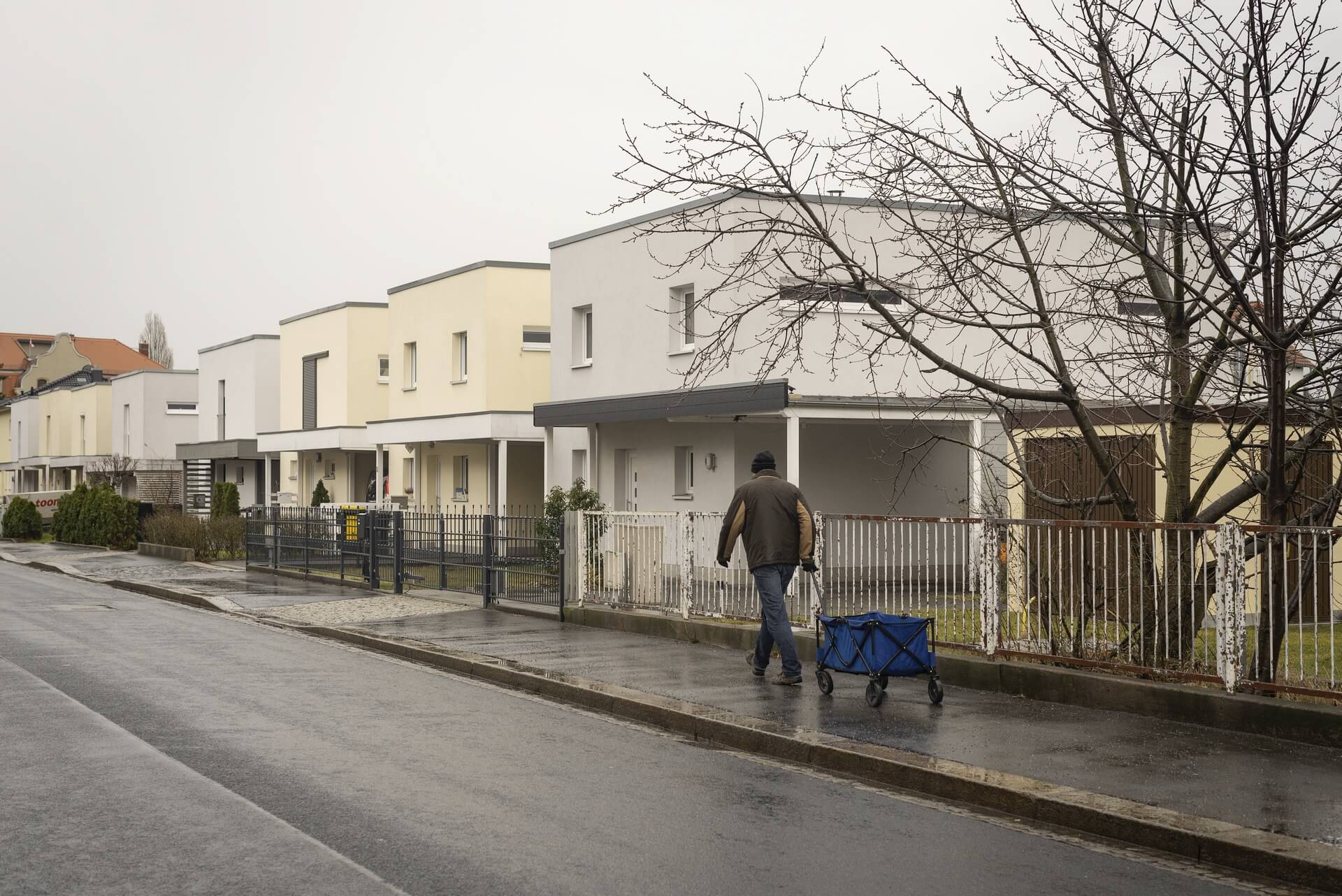
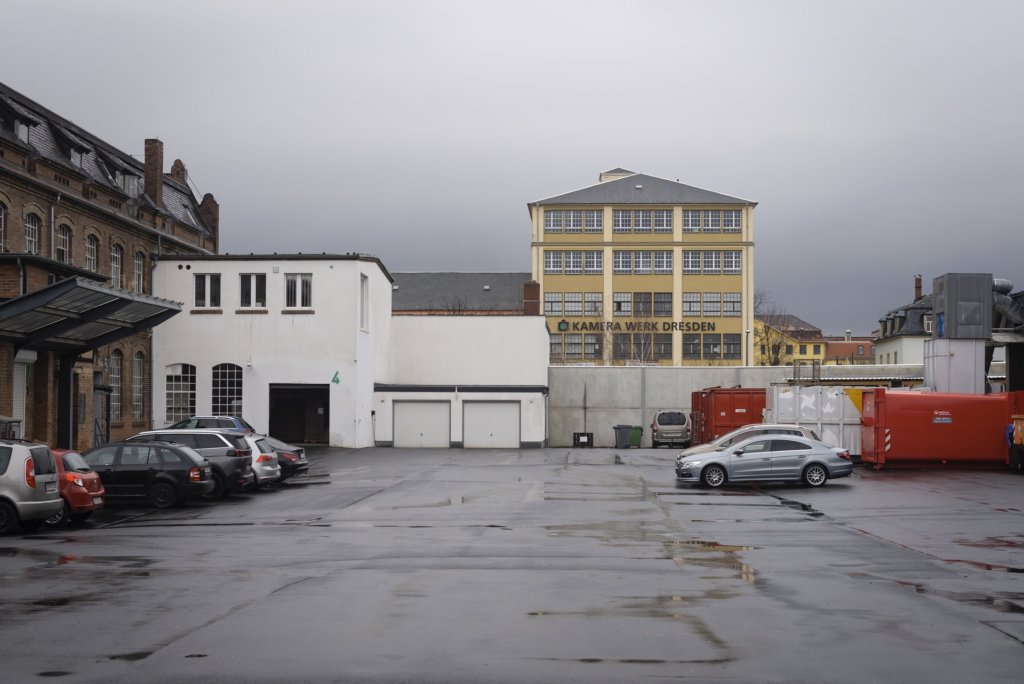
Reconstruction began on both sides of the Neisse, and in Guben the textile industry was successfully revived under socialist auspices. At the beginning of the 1960s, the Guben chemical fibre factory was built and, with over 8,000 jobs, became the city’s largest employer until 1990. In order to meet the immense demand for labour, a large prefabricated housing area was built, as was typical of the GDR. From 1961, the town was officially named Wilhelm-Pieck-Stadt Guben, after the first and only president of the GDR who was born here.
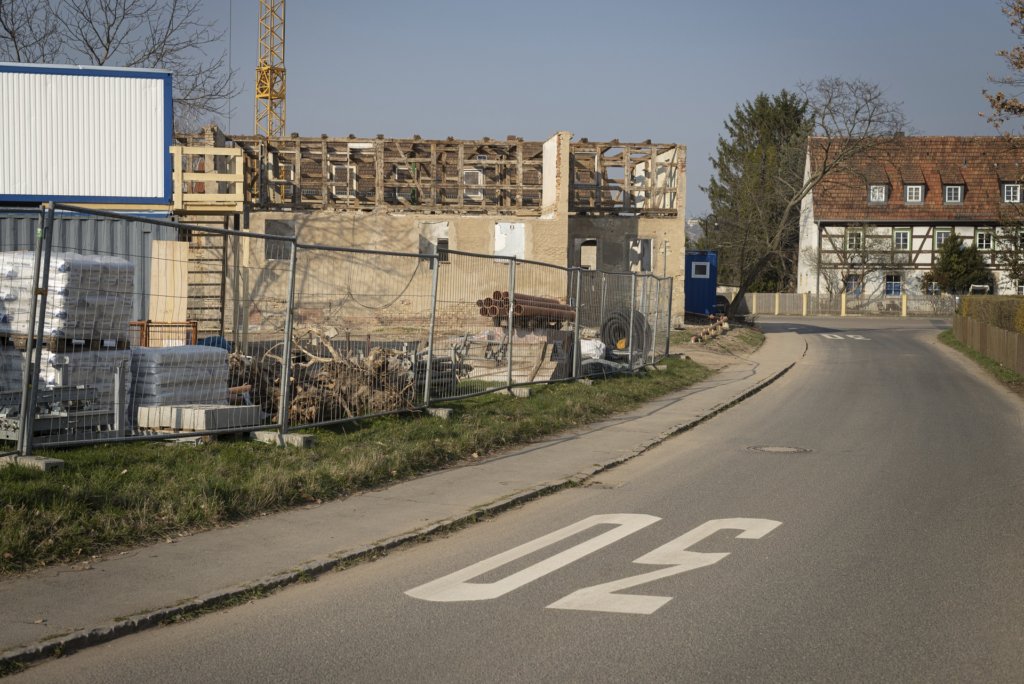
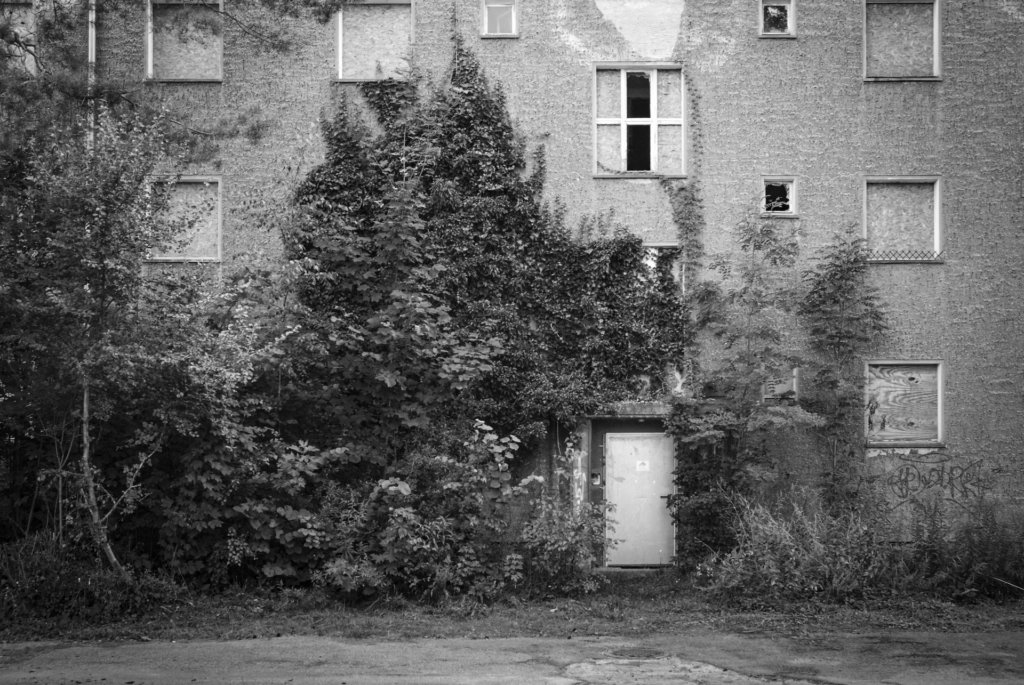
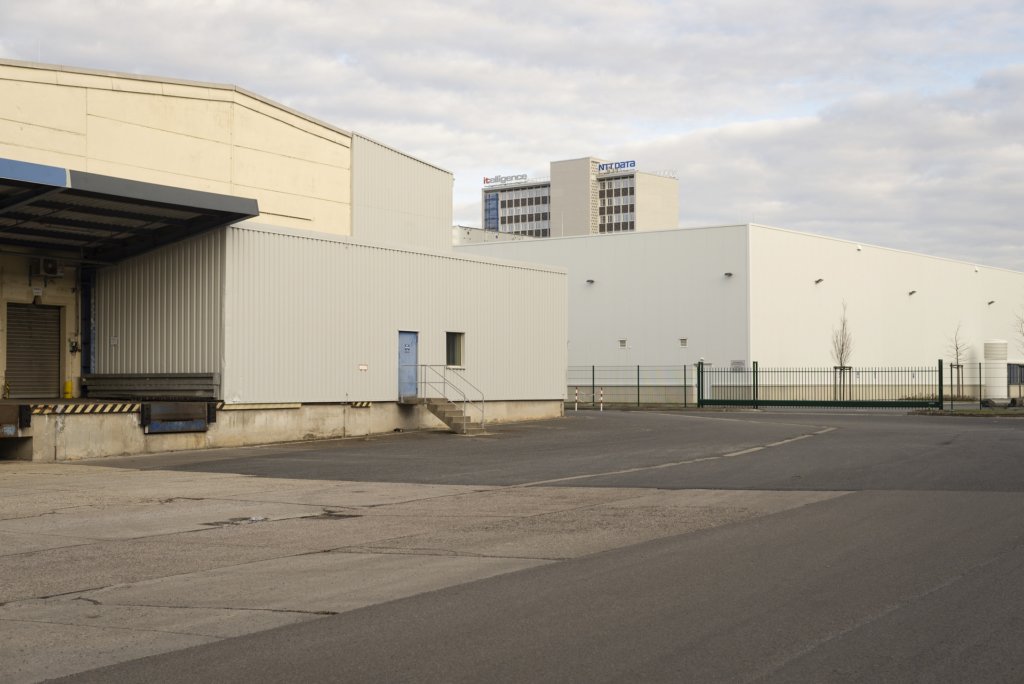
The peaceful revolution in autumn 1989 swept away the GDR, and with the political and economic unification of Germany in 1990, the next phase of Guben’s decline began. Almost all the industrial companies were closed down because they were unable to compete. Lack of work and prospects drove the inhabitants out of their town, the number of inhabitants halved in the following 30 years from 32,000 at the end of the GDR to a good 16,000 in 2020. The average age is over 50.
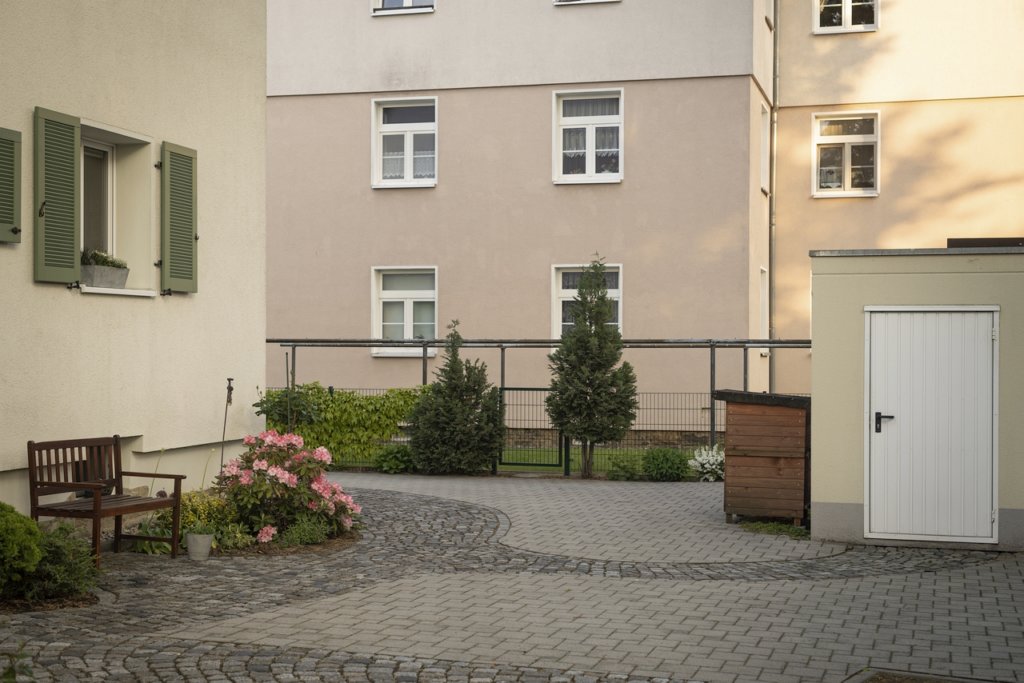
With Poland’s accession to the European Union in 2004 and to the Schengen Agreement in 2007, border controls were also abolished, and Guben and Gubin are striving for rapprochement and joint shaping of the future as the “Euro City Guben-Gubin” project. Recently, the trend towards migration was stopped. The settlement of new industrial companies was announced, important in a city whose largest private employers include the Gunther von Hagens Plastinarium, which produces anatomical specimens from human cadavers.
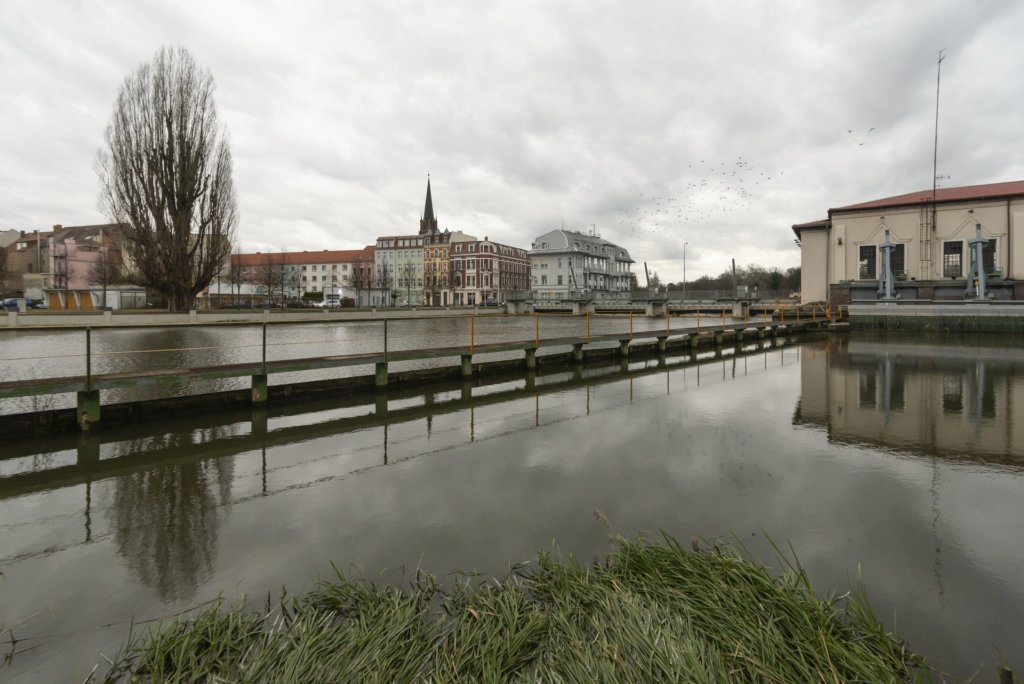
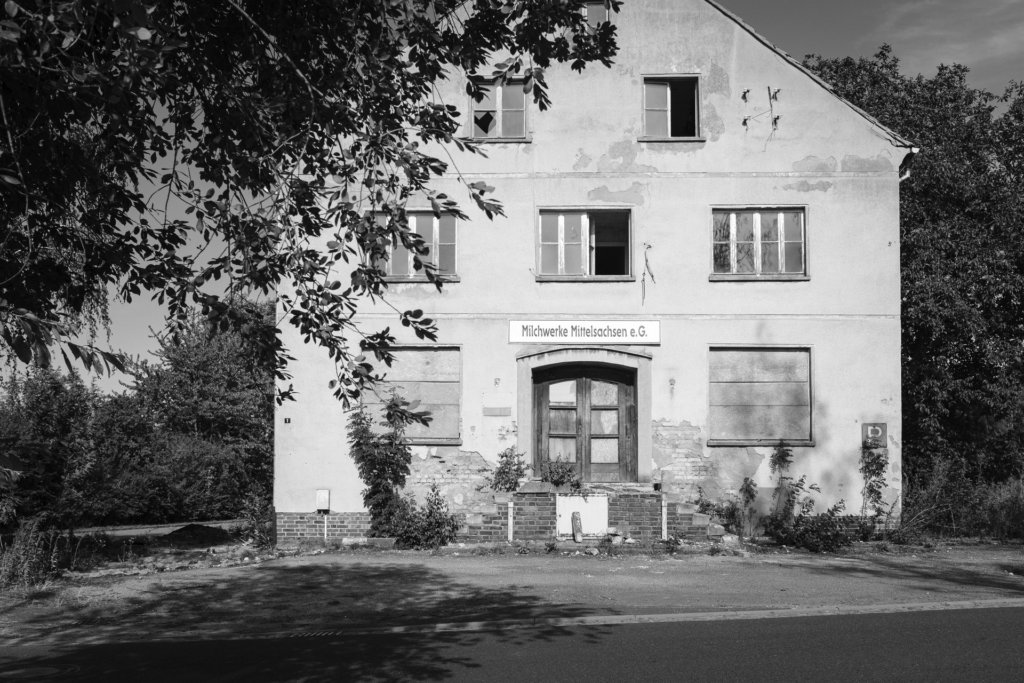
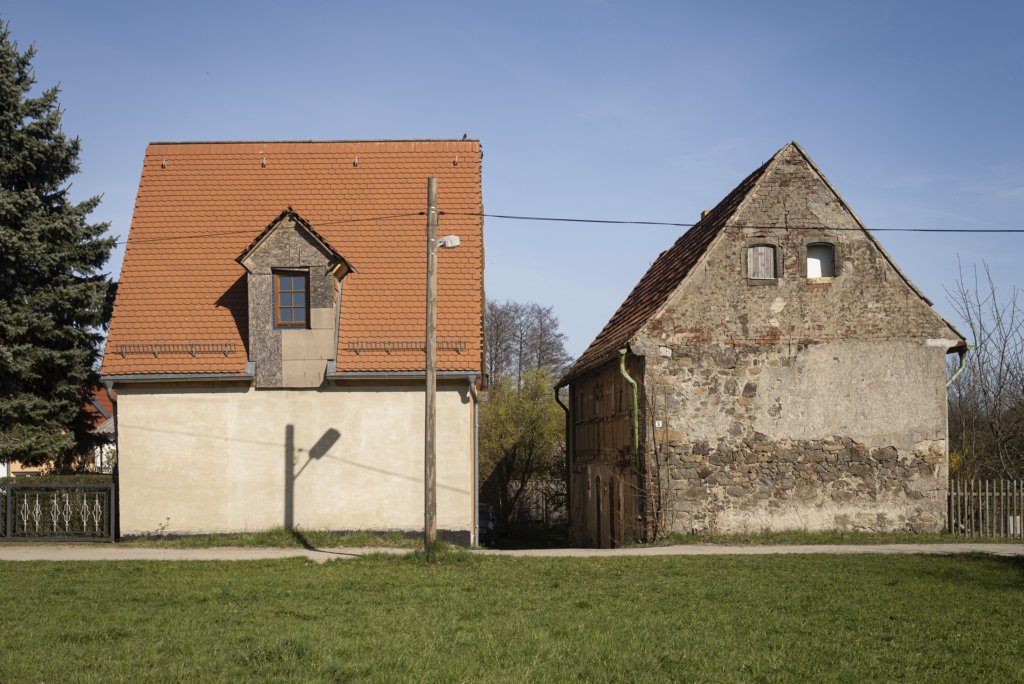
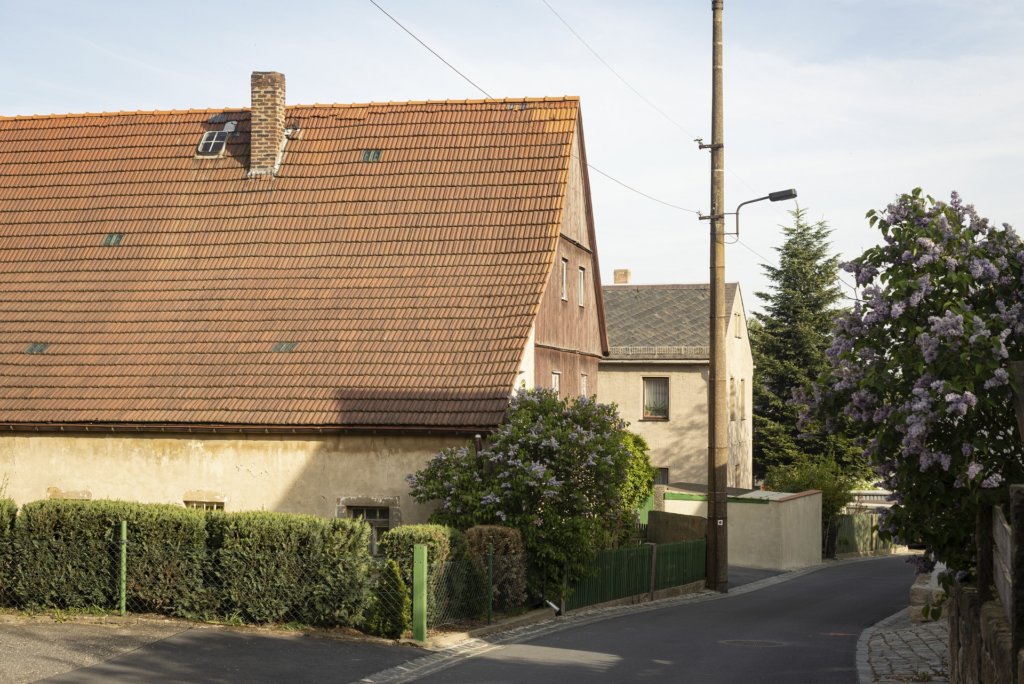
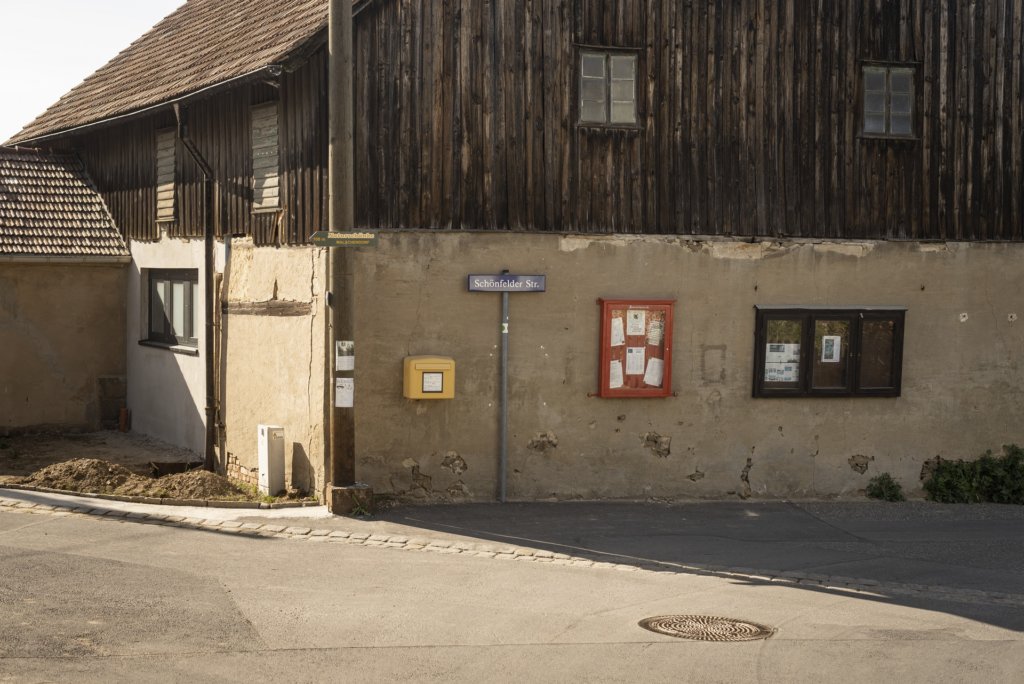
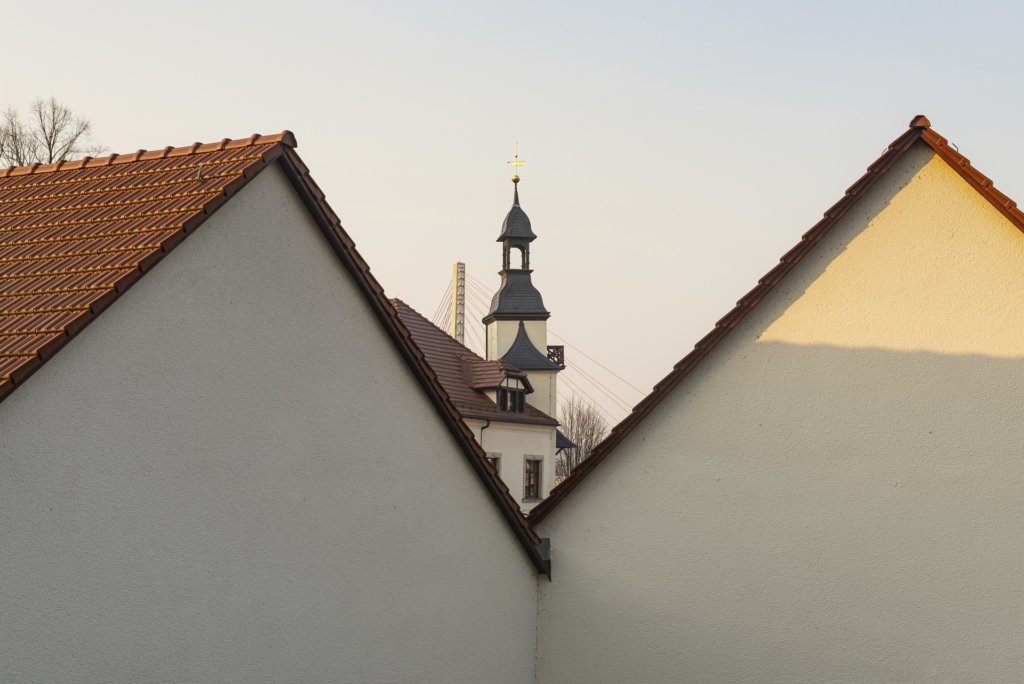
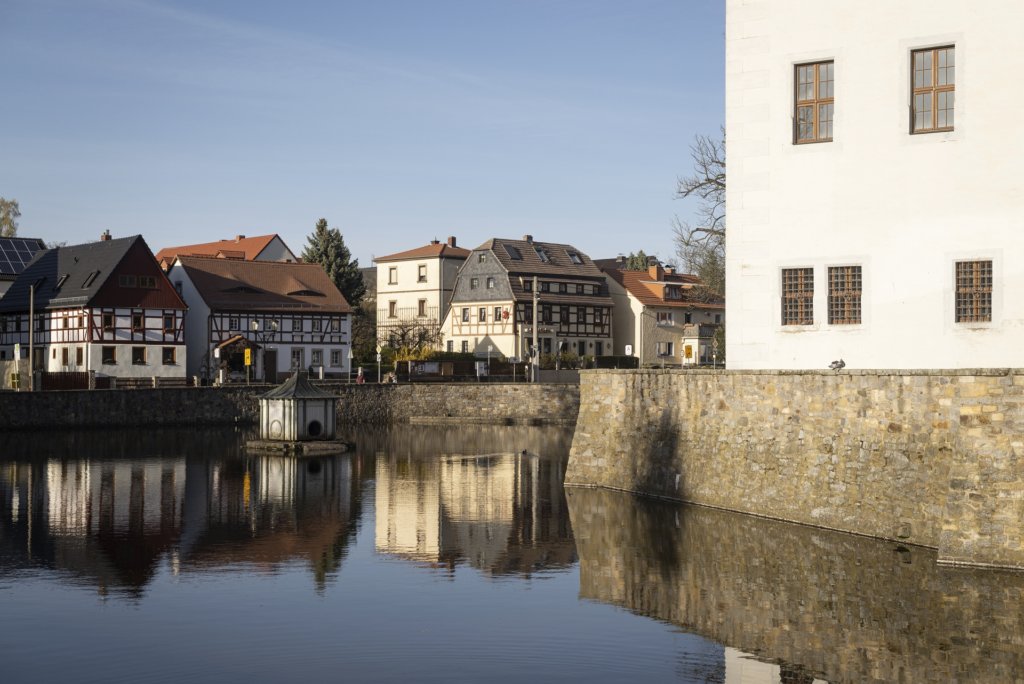
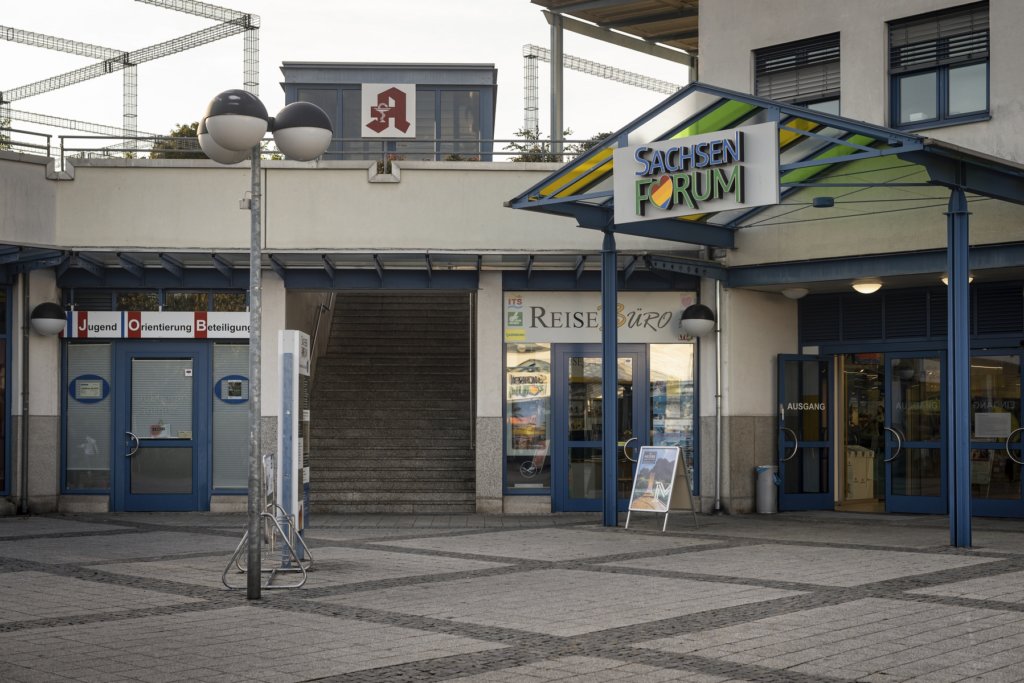
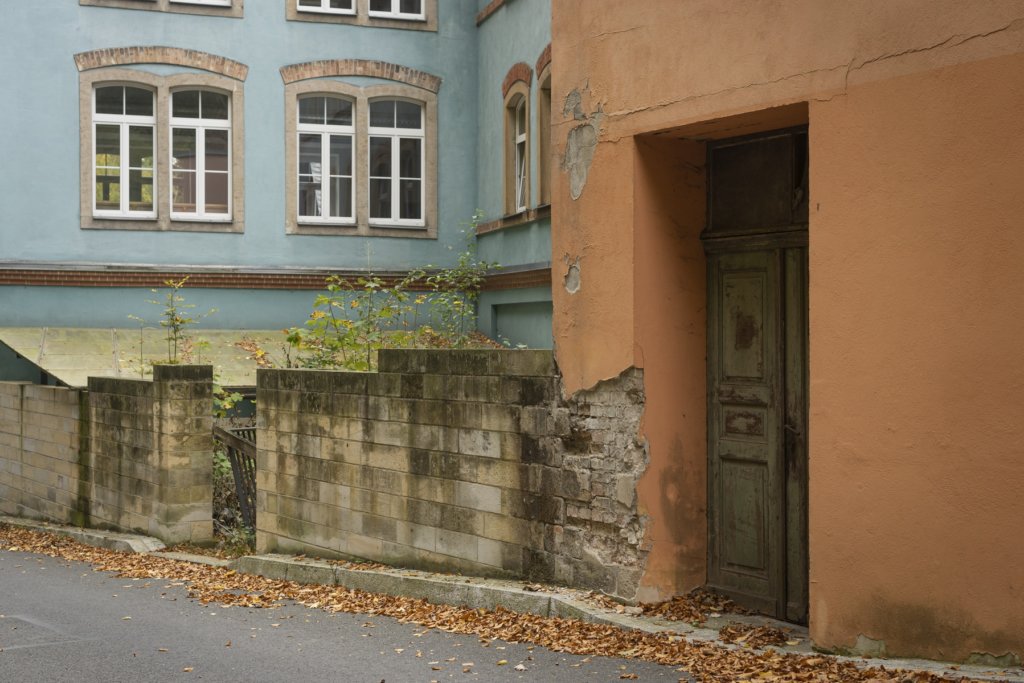
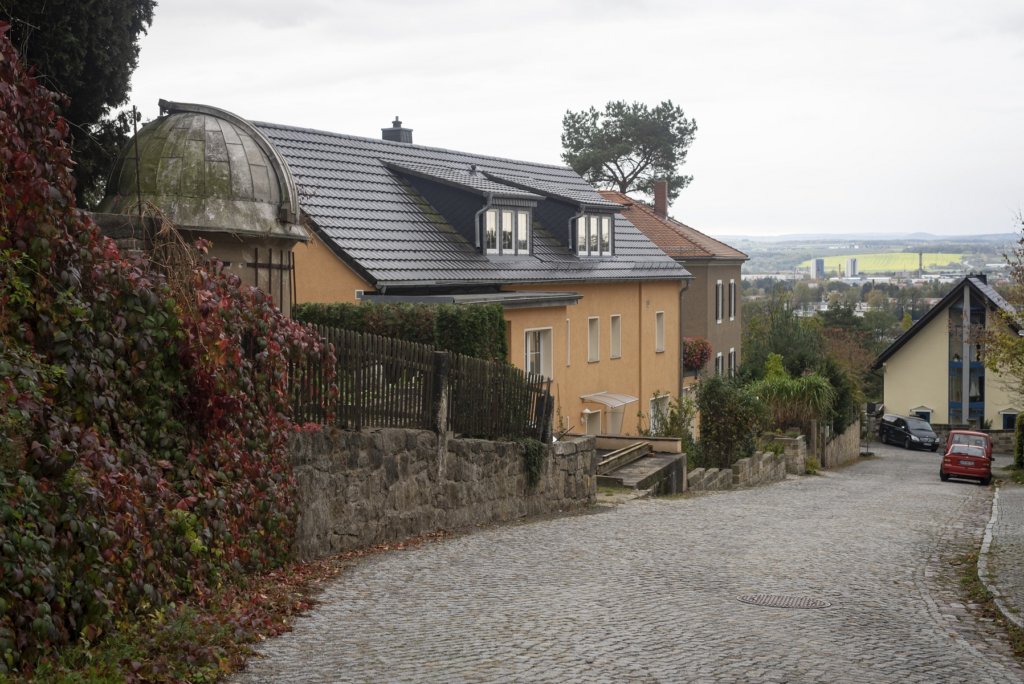
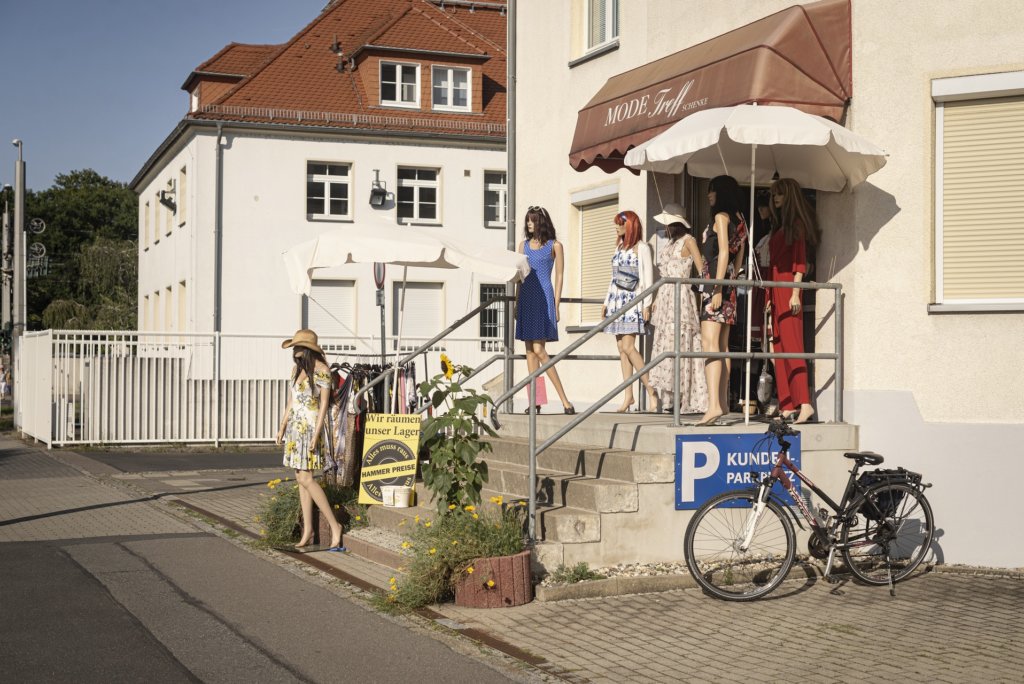
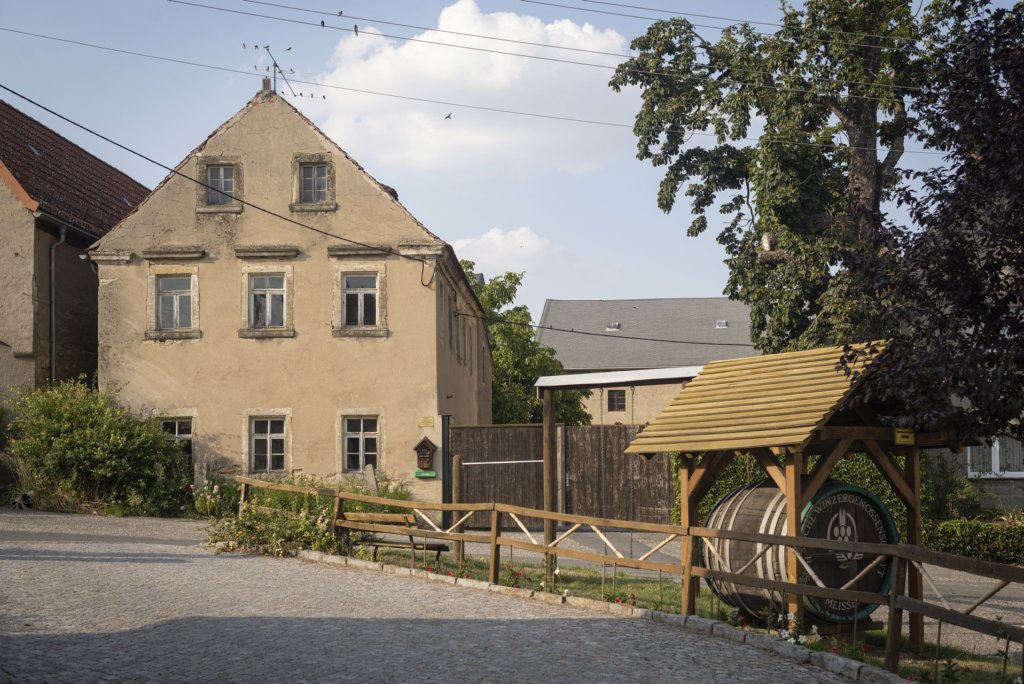
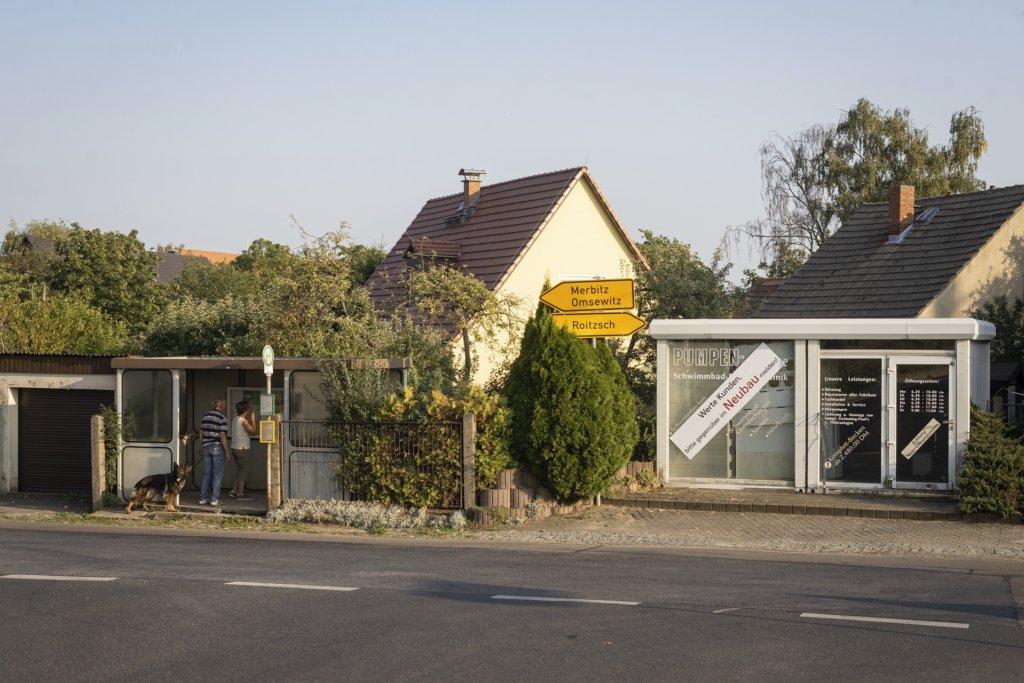
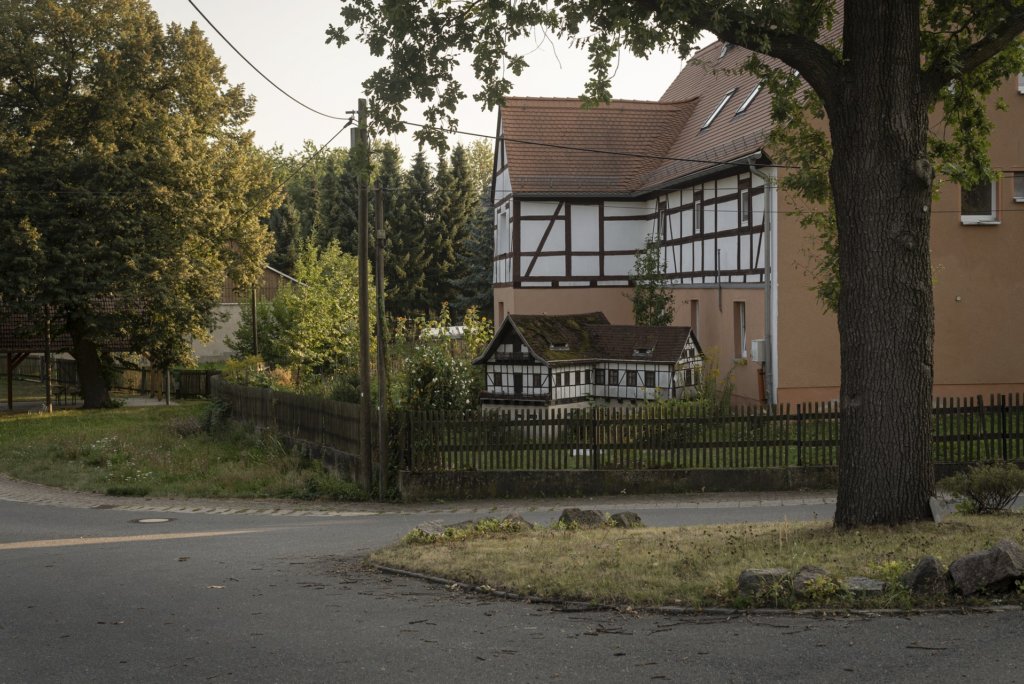
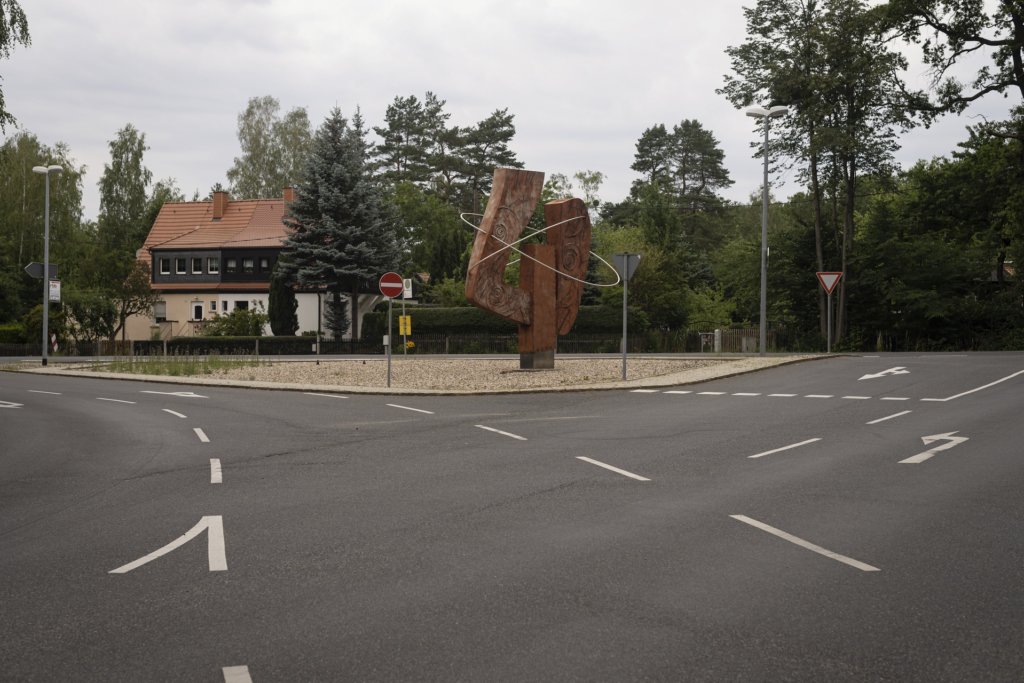
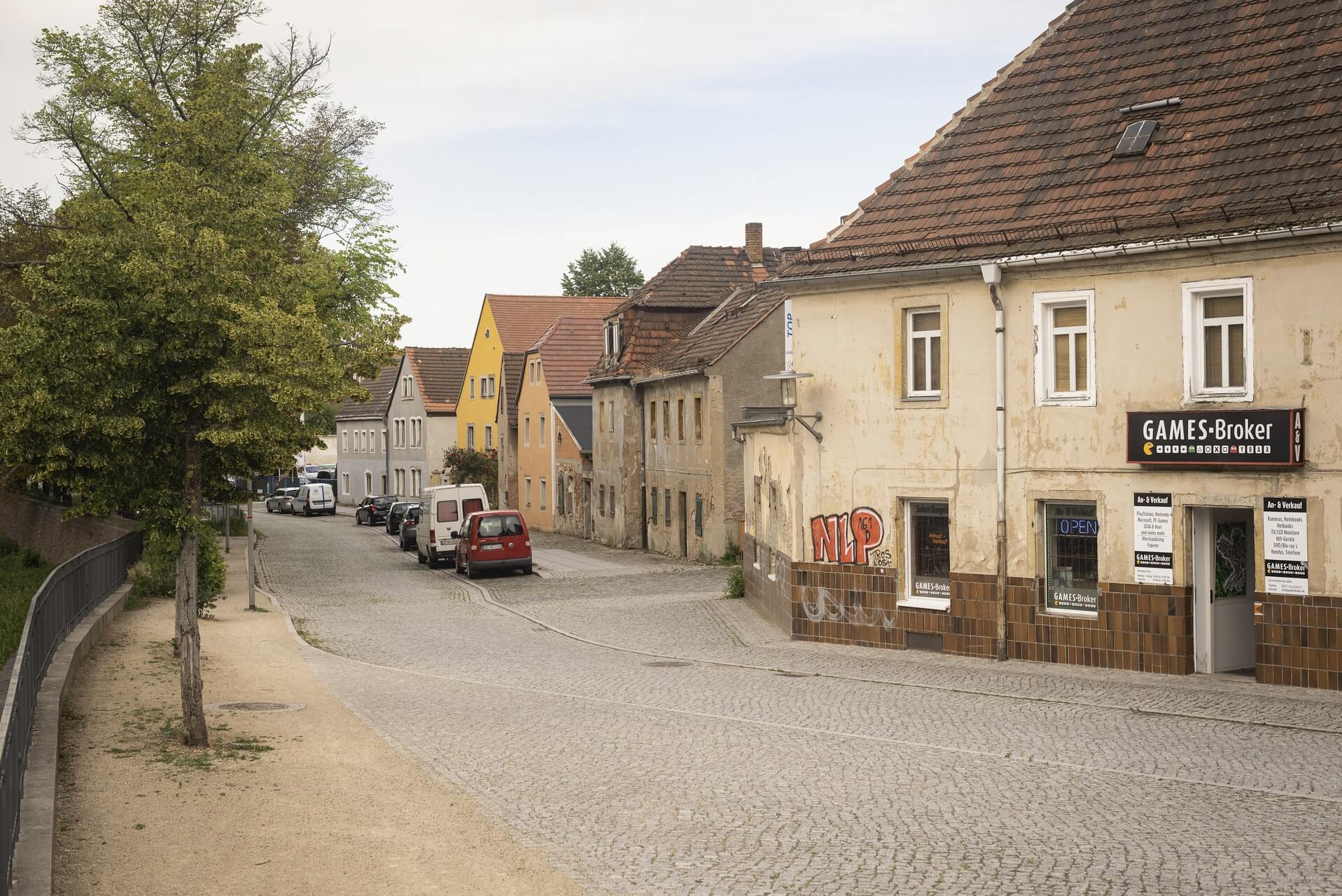
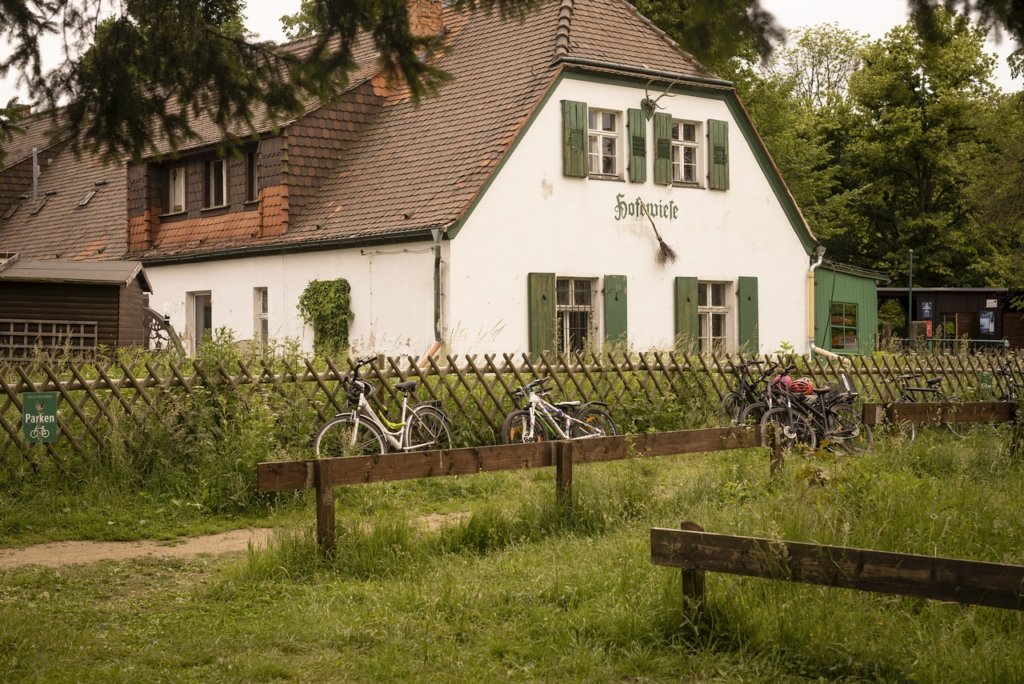
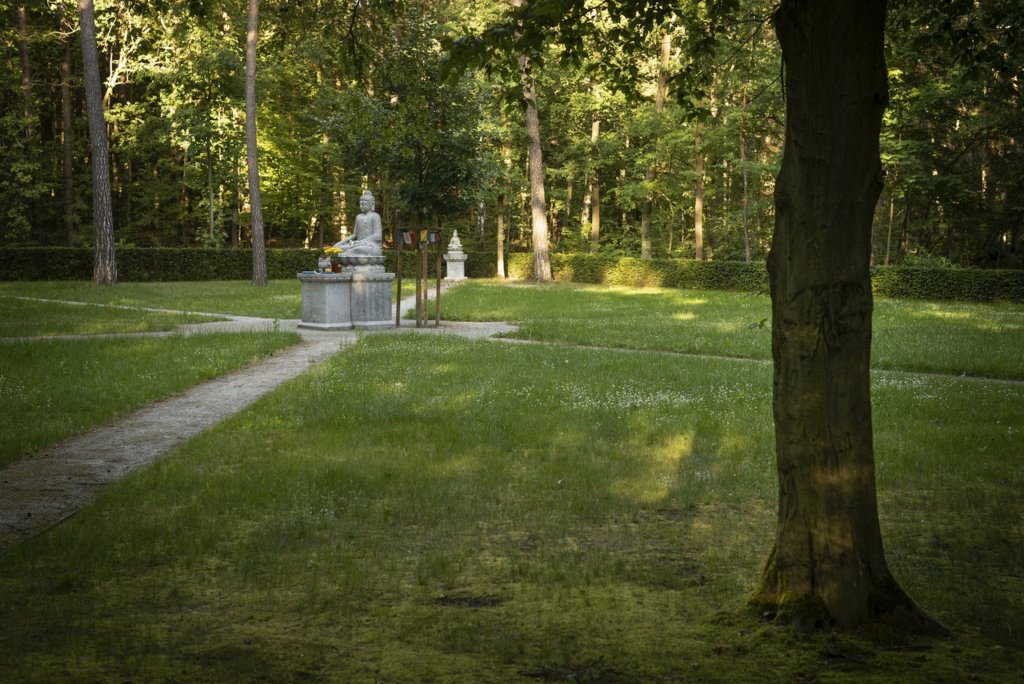
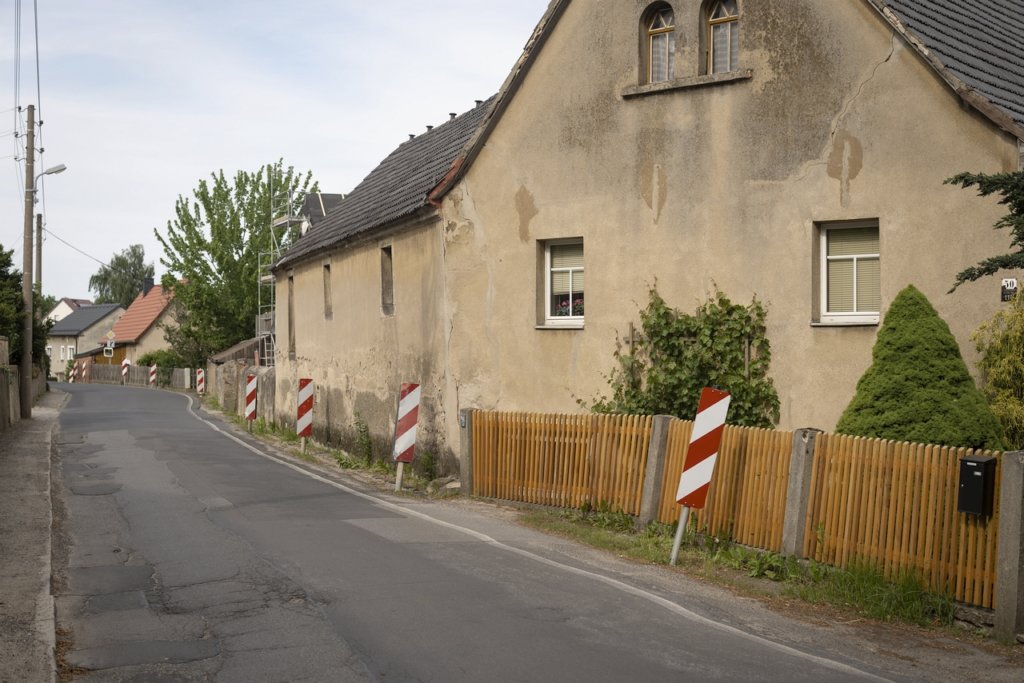
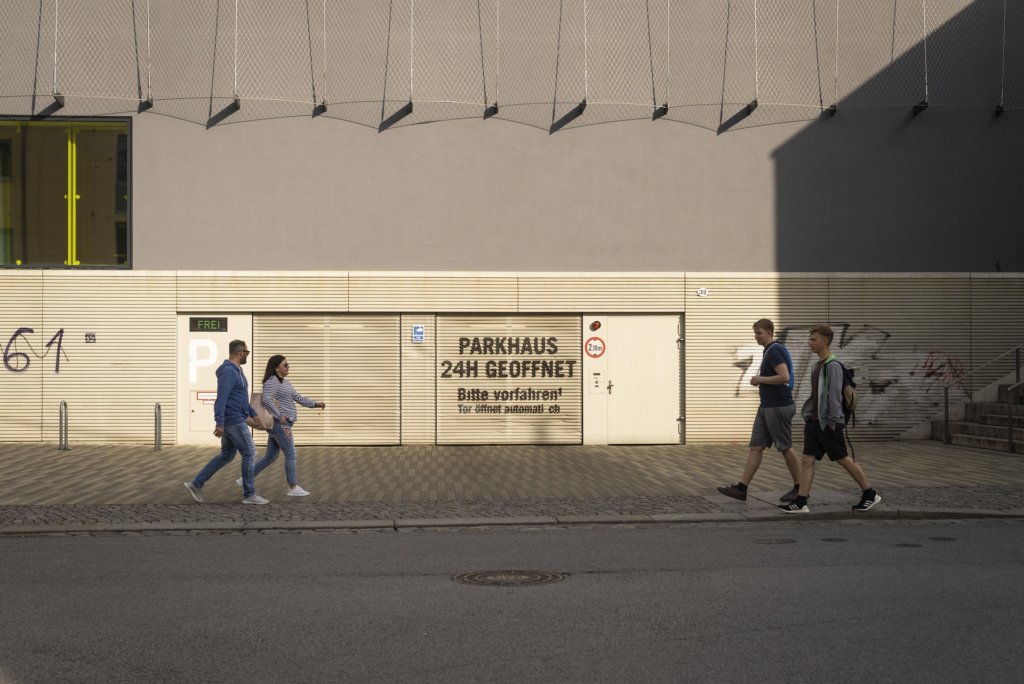
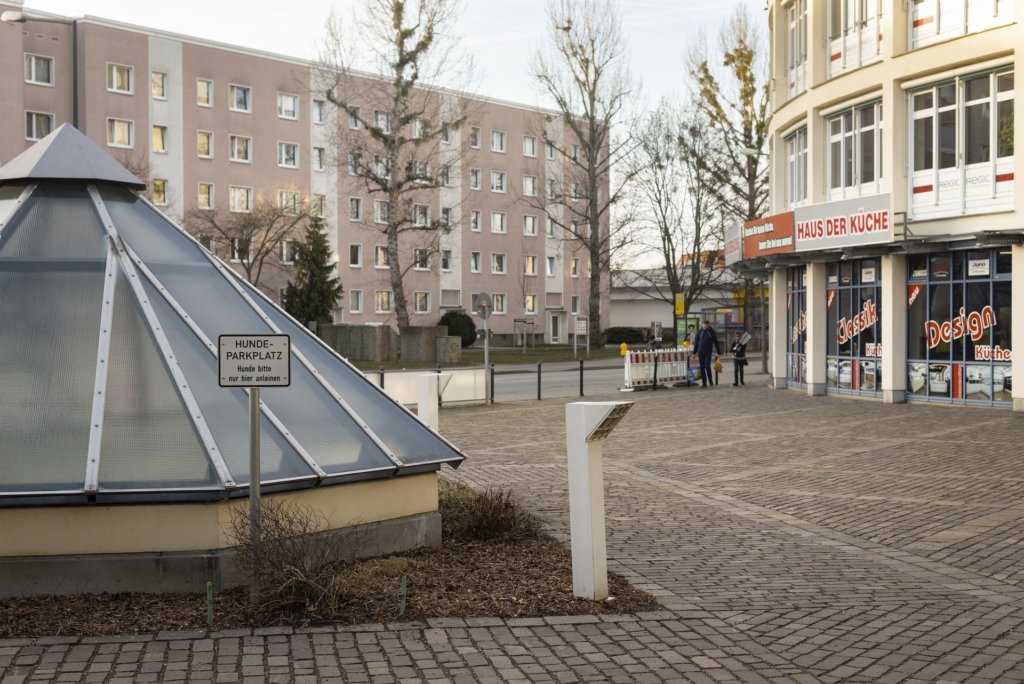
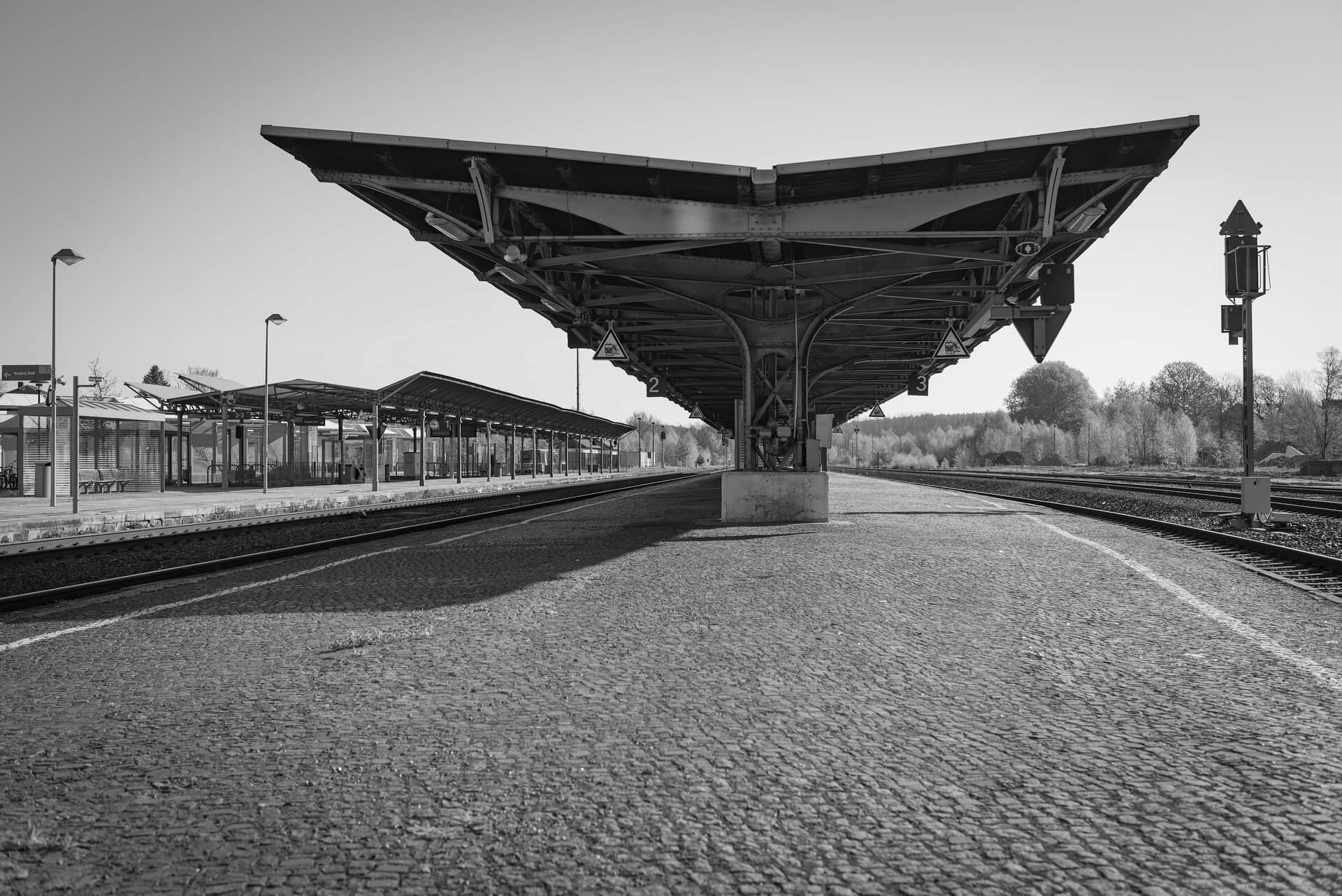
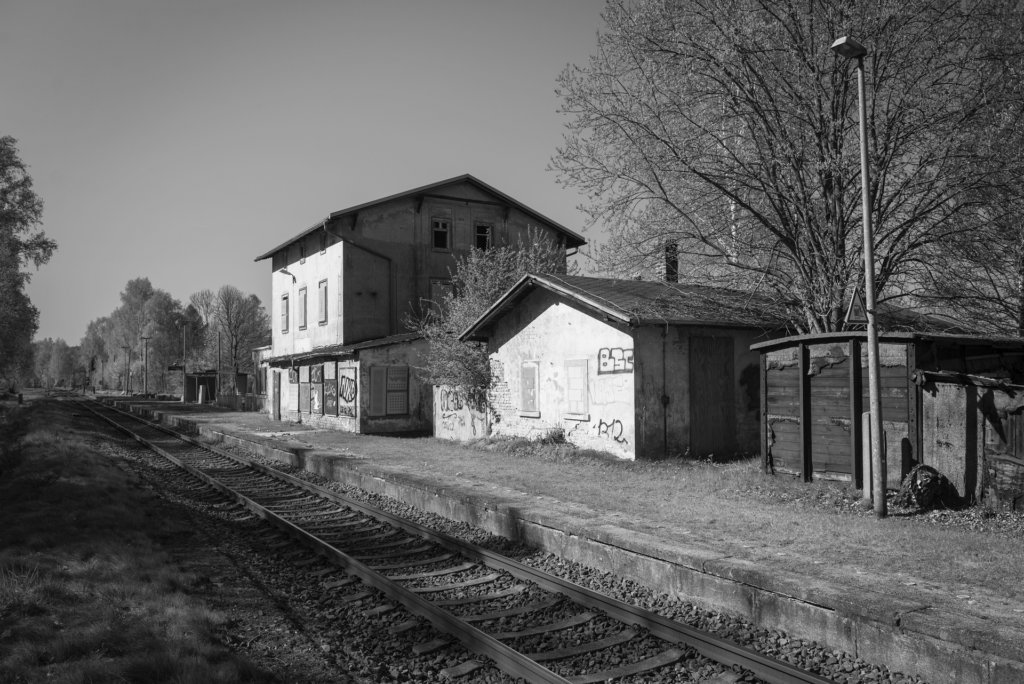
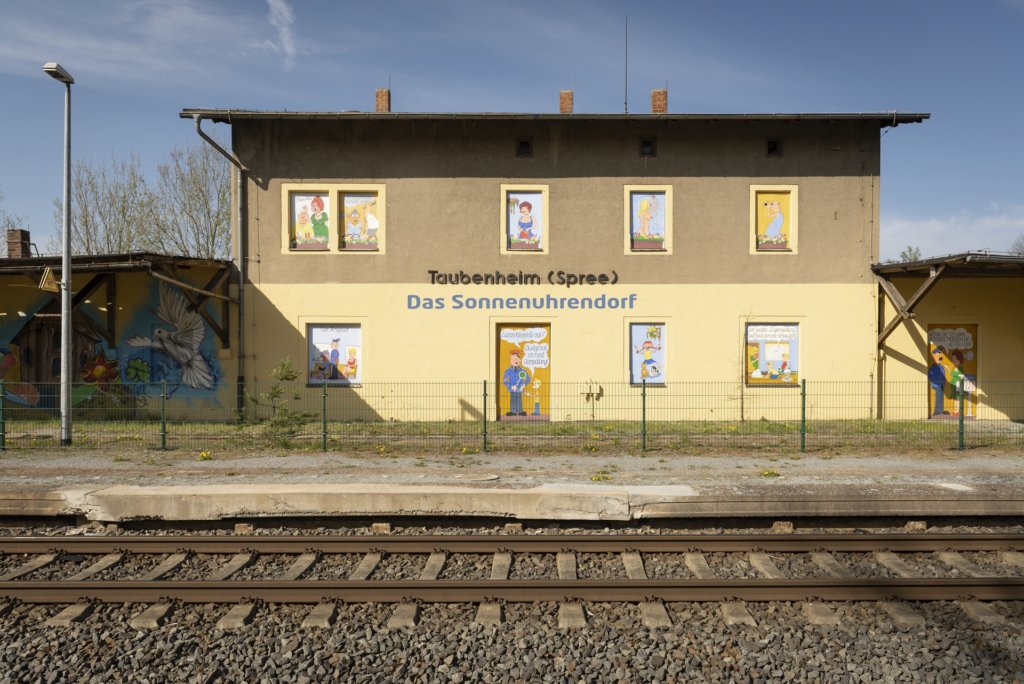
The will to create a liveable, border-crossing small town in spite of all the difficulties is visible, yet one also encounters signs of decay everywhere.
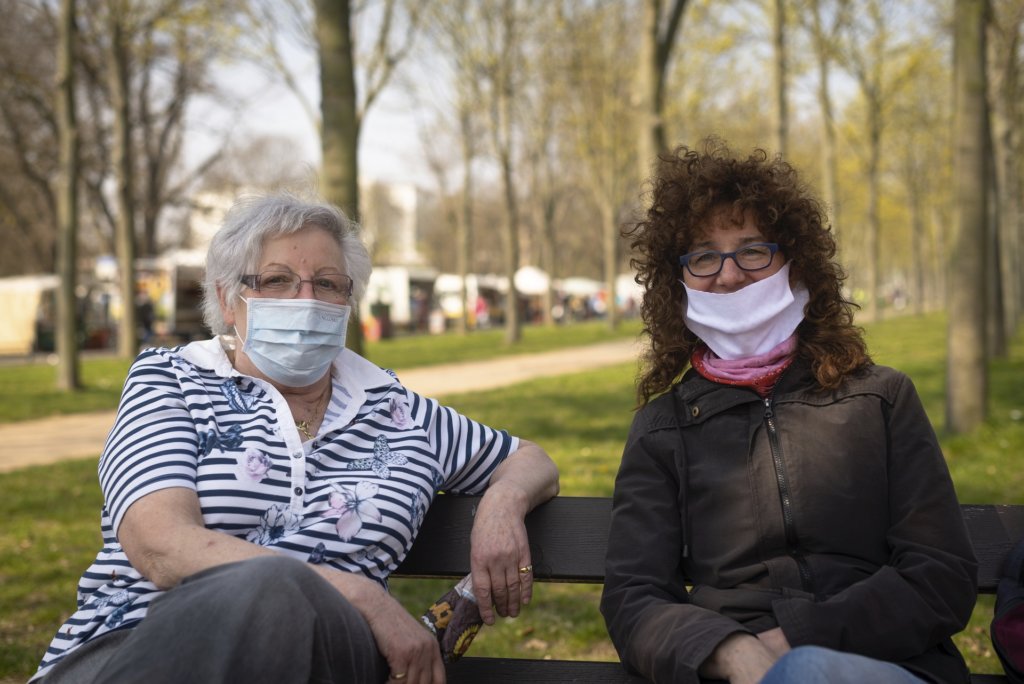
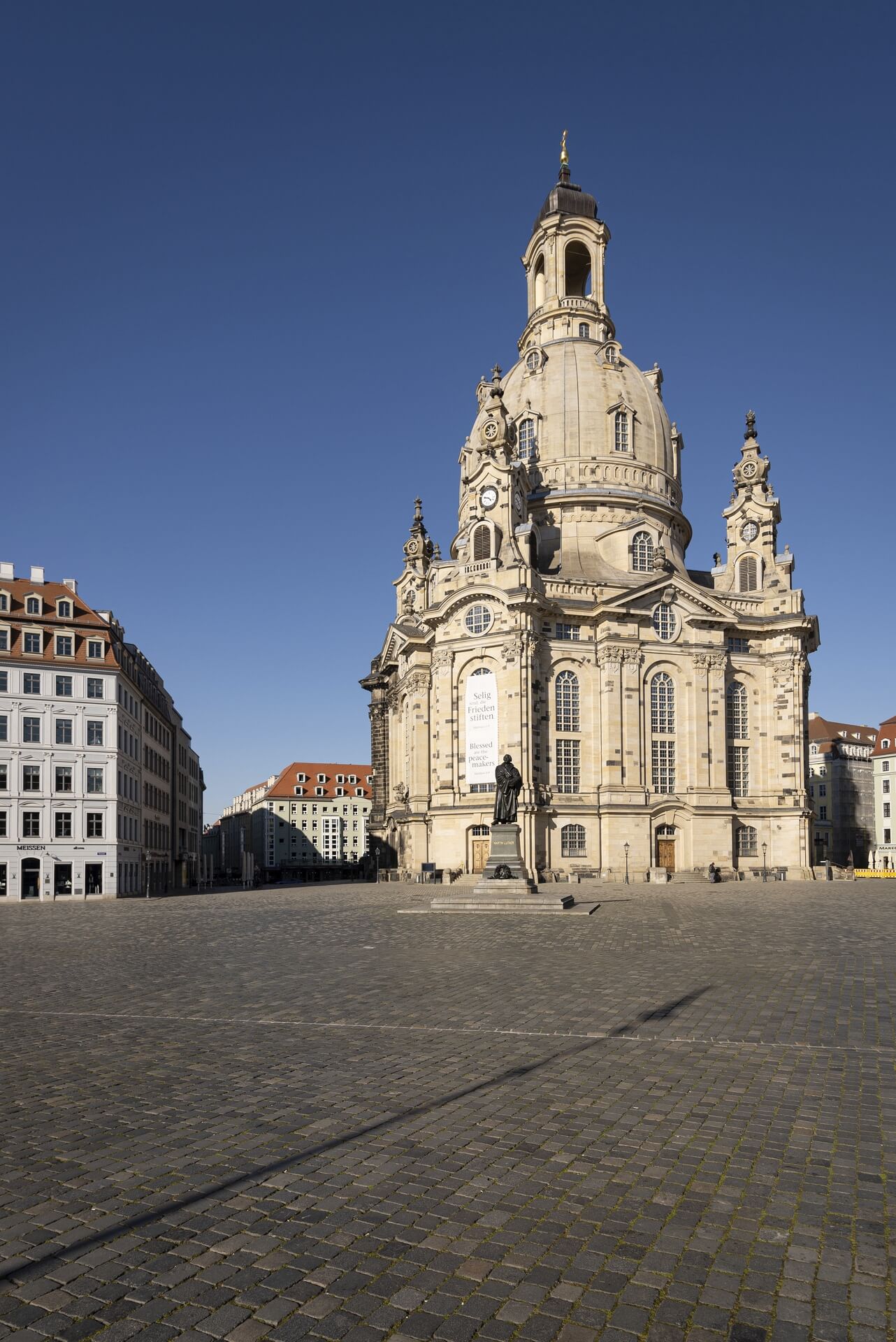
The photo series was taken on four days around the turn of the year 2021/2022. It soberly documents the state of affairs on both sides of the border; in most cases, the attentive viewer will be able to assign the photographs to Guben or Gubin.